
The reduced growth adds less to the growth inhibitor thus eliminating the perceived need. What happens is that the growth inhibitor works in a shorter time frame reducing growth.The annoying part of this structure is the delay associated with the inhibitor avoidance interaction with the growth inhibitor. This inhibitor avoidance will, after some delay, reduce the growth inhibitor. As the growth inhibitor interacts with a defined standard it develops a perceived need for action to develop some sort of inhibitor avoidance.

This system can be enabled to grow more if the growth inhibitor is reduced.This growth inhibitor subsequently impedes growth. As growth moves in the desired direction, it also influences an increase in some growth inhibitor. Growth sooner or latter produces some effect which tends to limit the growth. As was indicated in the Balancing Loop areas of concern, noting growth forever.The resultant growth then simply influences more of the same growing action, producing the reinforcing growth characteristic. The growing action which initiates this structure influences an increase in growth.The nasty thing about this structure is that the two balancing loops form a single reinforcing loop that inhibits growth. if the node in which the link starts increases, the other node decreases, and vice versa.Įdit this Diagram Cause Loop Diagram Example – Growth and InvestmentĪ Growth and Underinvestment structure is simply an elaborated Limits to Growth structure where the growth inhibitor is part of another Balancing Loop with an external standard and some delay. A negative causal link means the two nodes change in opposite directions, i.e. Similarly, if the node in which the link starts increases, the other node increases as well. if the node in which the link starts decreases, the other node also decreases. A positive causal link means the two nodes change in the same direction, i.e. A link marked positive indicates a positive relationship and a link marked negative indicates a negative relation. Nodes represent the variables and edges are the links that represent a connection or a relation between the two variables. The diagram consists of a set of nodes and edges. It becomes a model of system behaviors that create the outcome of the system.Ī causal loop diagram (CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are interrelated. People can point at the arrows in the loop that are reinforcing the problem instead of pointing at people. The neat thing about causal loops is it is depersonalizing. When finished you have a diagram of the positive and negative reinforcements which describe the system of behavior. Causal loops show the interrelation causes and their effects.
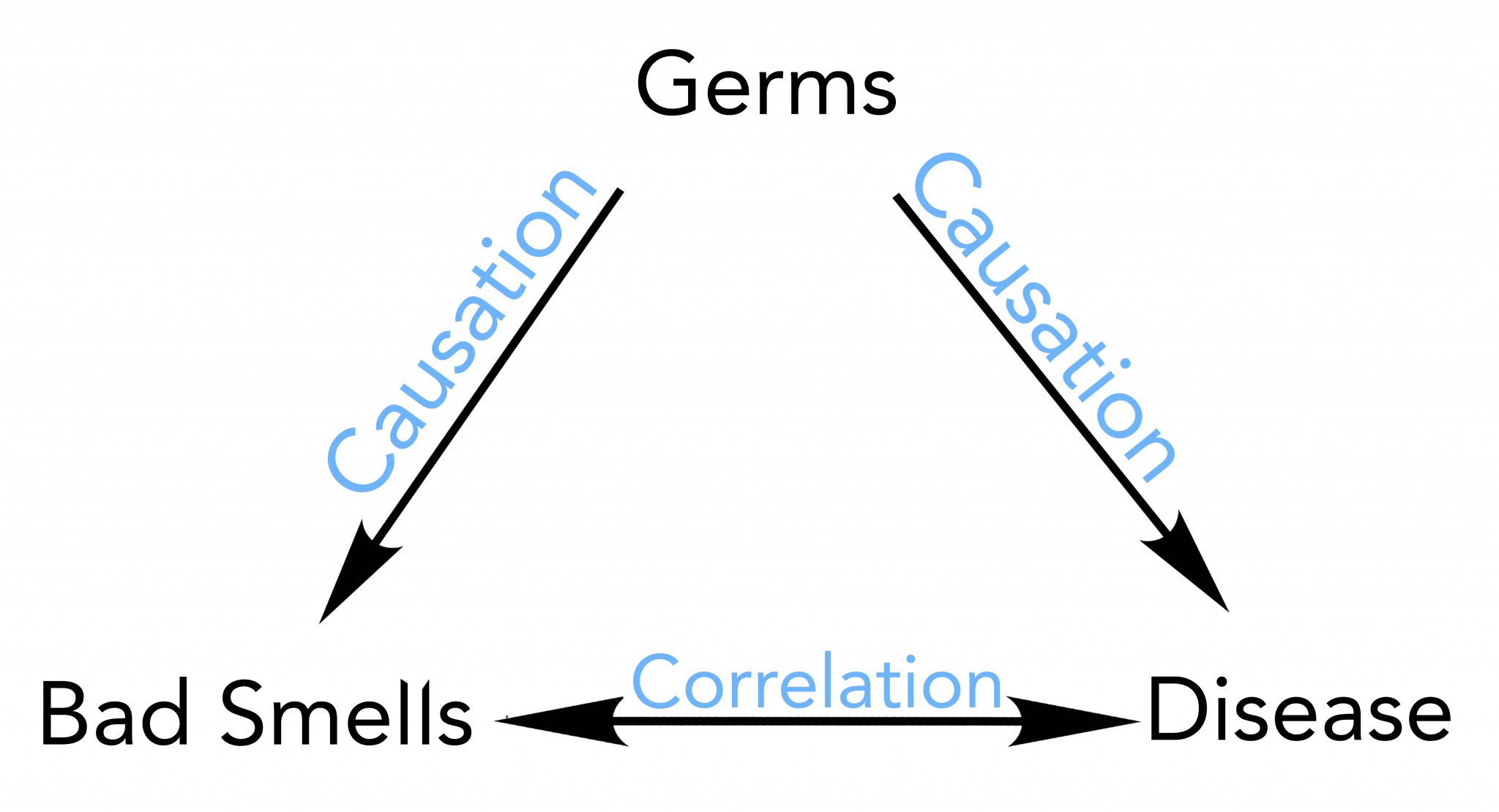
Fishbone diagrams may elicit the categories of causes that impact a problem. Causal loops diagrams (also known as system thinking diagrams) are used to display the behavior of cause and effect from a system’s standpoint.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
